PCOS is a condition in which the imbalance of hormones leads to the formation of one or more cysts inside the ovaries. These cysts target the whole body of a woman creating a number of complications showing its presence. These complications include:
- Glucose level fluctuations
- Menstrual irregularities
- Infertility
- Skin disorders such as acne, skin patches
- Hair disorder such as alopecia, facial hair growth
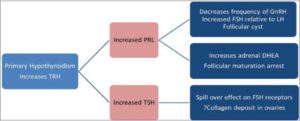
- Thyroid
- Obesity
- Endometrial cancer, etc
It has been demonstrated that approximately 34% of women with PCOS have depression compared to 7% of women in the general population and around 45% have anxiety, compared to only 18% of the general population.
These symptoms are so over expressive that within a short period of time, they start to target the psychological condition of a woman. When the mental state of a woman is affected in the form of stress & depression, the brain cells start to actively participate to advance the effect of cysts to a much higher level. This worsens the state of PCOS.
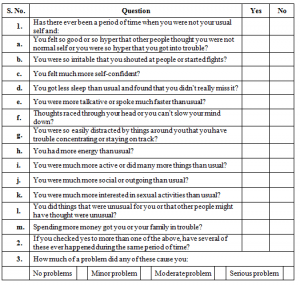
Research shows that PCOS gives rise to a variety of emotional and mental conditions such as
- Anxiety
- Panic attacks
- Depression
- Difficulty concentrating
- Fatigue
- Mood swings
- Chronic stress
- Eating disorders
HOW PCOS AFFECTS MENTAL HEALTH?
As in the mechanism of PCOS, higher testosterone (androgen) levels in the ovaries give rise to the development of cysts. Testosterone tends to inhibit the maturation of follicle containing egg. Thus, immature follicle becomes cyst.
It has been demonstrated by animal studies that these high levels of testosterone in PCOS women affect that region of the brain, which is responsible for emotions and behavior. They observed that high testosterone doses in animals significantly interfered with the activity of a gene in the brain region called amygdala that regulates the androgen receptor. They also identified alterations in the receptors for a form of estrogen due to high testosterone doses, as well as changes in the genes that regulate serotonin and GABA – neurotransmitters involved in the control of anxious behavior.
MANAGEMENT OF MENTAL HEALTH IN PCOS
It is clear from the reported data that women with PCOS are at risk of a wide range of significant psychological difficulties, which lower the quality of life also. Thus, treatment of PCOS is at extreme need to prevent physical and psychological issues.
A healthy lifestyle, nutritious diet, plentiful exercise and targeted nutritional supplements and/or prescription medications can help to bring the PCOS psychological issues under control.
Anti-androgens can also be consumed on prescription by doctor. Anti-androgens help to lower testosterone levels in the body. Normal levels of testosterones in women do not target the uncontrolled activity of amygdale (brain region for emotion & behavior) in the brain. This strategy will help to improve psychological condition in the women with PCOS. Other management measures include:
- Management of skin issues: Skin provides feminism to the women. Any changes in skin lead to depressive and stressful behavior in women. During PCOS, skin problems are taken as one of the symptoms. They are always taken as an outcome in PCOS. Treatment of skin issues such as acne & skin patches contributes in the management of mental health in women. Skin issues can be managed with the help of either natural remedies or by dietary modifications or by prescription medications. Any of the treatment measure can help resolve the skin issue.
- Management of hair loss: Another outcome of PCOS which adds-in towards depression and anxiety is “hair loss”. Management of hair loss can be done by consumption of anti-androgens because hair loss due to PCOS involves the over-production of androgens (testosterone) in the body. Testosterones interfere in the normal cycle of hair-follicle growth due to which hair density is also thickened. Thus, anti-androgens lower the production of testosterone and help in the growth cycle of hair follicles.
- Obesity management: Obesity is a major reason behind depression and anxiety in PCOS women. Healthy lifestyle, controlled diet and regular exercise help to control obesity. Weight loss medications can also be consumed to treat obesity. According to the reported studies, participation in physical activity programs is associated with lowering obesity and depressive symptoms and improvements in quality of life.
- Cyst management: Reduction of the cysts in PCOS is the primary line-of-treatment. This can be achieved by controlling testosterone levels in the body along with management of insulin resistance. Testosterones can be controlled by either anti-androgens or testosterone suppressing drugs. Both of these treatment regimens can help to lower cyst size and cyst number which will automatically help to manage menstrual irregularities and infertility problems. They might contribute well to lower mental health issues in PCOS.
These management strategies are a key towards improvement in the mental health issues. By controlling PCOS as early as possible, mental health issues can also be controlled.
It has been reported that fenugreek is an effective remedy to treat PCOS patients. It is clinically proven safe and effective in the management of PCOS. It has been observed that Furocyst® (fenugreek seed extract) significantly reduced the cyst size, showed complete dissolution of the cysts and reported regular menstrual cycle on completion of the treatment. It also increased insulin sensitizing activity & peripheral utilization of insulin thus helped to manage PCOS.
REFERENCES
- http://www.huffingtonpost.co.uk/holly-whiting/the-silent-disorder-pcos_b_8359900.html
- https://www.pcos.com/pcos-and-emotional-mental-disorders/?nabe=5589080592613376:1&utm_referrer=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.google.co.in%2F
- https://jeanhailes.org.au/health-a-z/pcos/emotions
- http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/301822.php
- http://www.yeoldejournalist.com/study-sheds-light-on-link-between-pcos-and-mental-health/
- http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/811010
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Melissa_Himelein/publication/6750579_Polycystic_ovary_syndrome_and_mental_health_A_review/links/54134b040cf2bb7347db207e.pdf
- https://bmcwomenshealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1472-6874-14-51
- http://www.rheumatologynews.com/fileadmin/content_pdf/san/scms_pdf/vol28_i1_Hair_Loss.pdf




































 Tender, warm, swollen joints
Tender, warm, swollen joints





