What Is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer develops in a man’s prostate, the walnut-sized gland just below the bladder that produces some of the fluid in semen. It’s the most common cancer in men after skin cancer. Prostate cancer often grows very slowly and may not cause significant harm. But some types are more aggressive and can spread quickly without treatment.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
In the early stages, men may have no symptoms. Later, symptoms can include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urinary stream
- Painful or burning sensation during urination or ejaculation
- Blood in urine or semen
Advanced cancer can cause deep pain in the lower back, hips, or upper thighs.
Enlarged Prostate or Prostate Cancer?
 The prostate can grow larger as men age, sometimes pressing on the bladder or urethra and causing symptoms similar to prostate cancer. This is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It’s not cancer and can be treated if symptoms become bothersome. A third problem that can cause urinary symptoms is prostatitis. This inflammation or infection may also cause a fever and in many cases is treated with medication.
The prostate can grow larger as men age, sometimes pressing on the bladder or urethra and causing symptoms similar to prostate cancer. This is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It’s not cancer and can be treated if symptoms become bothersome. A third problem that can cause urinary symptoms is prostatitis. This inflammation or infection may also cause a fever and in many cases is treated with medication.
Risk Factors You Can’t Control
 Growing older is the greatest risk factor for prostate cancer, particularly after age 50. After age 70, studies suggest that most men have some form of prostate cancer, though there may be no outward symptoms. Family history increases a man’s risk: having a father or brother with prostate cancer doubles the risk. African-Americans are at high risk and have the highest rate of prostate cancer in the world.
Growing older is the greatest risk factor for prostate cancer, particularly after age 50. After age 70, studies suggest that most men have some form of prostate cancer, though there may be no outward symptoms. Family history increases a man’s risk: having a father or brother with prostate cancer doubles the risk. African-Americans are at high risk and have the highest rate of prostate cancer in the world.
Risk Factors You Can Control

Diet seems to play a role in the development of prostate cancer, which is much more common in countries where meat and high-fat dairy are mainstays. The reason for this link is unclear. Dietary fat, particularly animal fat from red meat, may boost male hormone levels. And this may fuel the growth of cancerous prostate cells. A diet too low in fruits and vegetables may also play a role.
Myths About Prostate Cancer
 Here are some things that will not cause prostate cancer: Too much sex, a vasectomy, and masturbation. If you have an enlarged prostate (BPH), that does not mean you are at greater risk of developing prostate cancer. Researchers are still studying whether alcohol use, STDs, or prostatitis play a role in the development of prostate cancer.
Here are some things that will not cause prostate cancer: Too much sex, a vasectomy, and masturbation. If you have an enlarged prostate (BPH), that does not mean you are at greater risk of developing prostate cancer. Researchers are still studying whether alcohol use, STDs, or prostatitis play a role in the development of prostate cancer.
Can Prostate Cancer Be Found Early?
 Screening tests are available to find prostate cancer early, but government guidelines don’t call for routine testing in men at any age. The tests may find cancers that are so slow-growing that medical treatments would offer no benefit. And the treatments themselves can have serious side effects. The American Cancer Society advises men to talk with a doctor about screening tests, beginning at:
Screening tests are available to find prostate cancer early, but government guidelines don’t call for routine testing in men at any age. The tests may find cancers that are so slow-growing that medical treatments would offer no benefit. And the treatments themselves can have serious side effects. The American Cancer Society advises men to talk with a doctor about screening tests, beginning at:
- Age 50 for average-risk men who expect to live at least 10 more years
- Age 45 for men at high risk; this includes African-Americans and those with a father, brother, or son diagnosed before age 65
- Age 40 for men with more than one first-degree relative diagnosed at an early age
Screening: DRE and PSA
 Your doctor may initially do a digital rectal exam (DRE) to feel for bumps or hard spots on the prostate. After a discussion with your doctor, a blood test can be used to measure prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a protein produced by prostate cells. An elevated level may indicate a higher chance that you have cancer, but you can have a high level and still be cancer-free. It is also possible to have a normal PSA and have prostate cancer.
Your doctor may initially do a digital rectal exam (DRE) to feel for bumps or hard spots on the prostate. After a discussion with your doctor, a blood test can be used to measure prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a protein produced by prostate cells. An elevated level may indicate a higher chance that you have cancer, but you can have a high level and still be cancer-free. It is also possible to have a normal PSA and have prostate cancer.
PSA Test Results
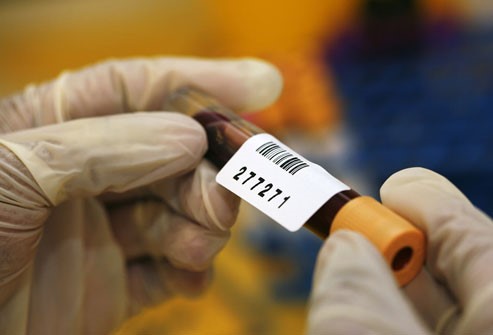 A normal PSA level is considered to be under 4 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) of blood, while a PSA above 10 suggests a high risk of cancer. But there are many exceptions:
A normal PSA level is considered to be under 4 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) of blood, while a PSA above 10 suggests a high risk of cancer. But there are many exceptions:
- Men can have prostate cancer with a PSA less than 4.
- A prostate that is inflamed (prostatitis) or enlarged (BPH) can boost PSA levels, yet further testing may show no evidence of cancer.
- Some BPH drugs can lower PSA levels, despite the presence of prostate cancer, called a false negative.
If either a PSA or DRE test are abnormal, your doctor will order other tests.
Prostate Cancer Biopsy
 If a physical exam or PSA test suggests a problem, your doctor may recommend a biopsy. A needle is inserted either through the rectum wall or the skin between the rectum and scrotum. Multiple small tissue samples are removed and examined under a microscope. A biopsy is the best way to detect cancer and predict whether it is slow-growing or aggressive.
If a physical exam or PSA test suggests a problem, your doctor may recommend a biopsy. A needle is inserted either through the rectum wall or the skin between the rectum and scrotum. Multiple small tissue samples are removed and examined under a microscope. A biopsy is the best way to detect cancer and predict whether it is slow-growing or aggressive.
Biopsy and Gleason Score
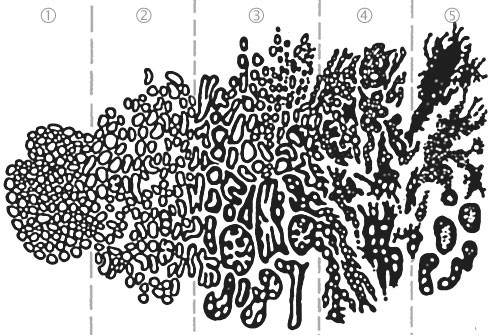 A pathologist looks for cell abnormalities and “grades” the tissue sample from 1 to 5. The sum of two Gleason grades is the Gleason score. These scores help determine the chances of the cancer spreading. They range from 2, less aggressive, to 10, a very aggressive cancer. Gleason scores helps guide the type of treatment your doctor will recommend.
A pathologist looks for cell abnormalities and “grades” the tissue sample from 1 to 5. The sum of two Gleason grades is the Gleason score. These scores help determine the chances of the cancer spreading. They range from 2, less aggressive, to 10, a very aggressive cancer. Gleason scores helps guide the type of treatment your doctor will recommend.
Prostate Cancer Imaging
 Some men may need additional tests to see if the cancer has spread beyond the prostate. These can include ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan (seen here). A radionuclide bone scan traces an injection of low-level radioactive material to help detect cancer that has spread to the bone.
Some men may need additional tests to see if the cancer has spread beyond the prostate. These can include ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan (seen here). A radionuclide bone scan traces an injection of low-level radioactive material to help detect cancer that has spread to the bone.
In the MRI scan shown here, the tumor is the green, kidney-shaped mass in the center, next to the prostate gland (in pink).
Prostate Cancer Staging
 Staging is used to describe how far prostate cancer has spread (metastasized) and to help determine the best treatment.
Staging is used to describe how far prostate cancer has spread (metastasized) and to help determine the best treatment.
- Stage I: Cancer is small and still within the prostate.
- Stage II: Cancer is more advanced, but still confined to the prostate.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to the outer part of the prostate and nearby seminal vesicles.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to lymph nodes, nearby organs or tissues such as the bladder or rectum, or distant organs such as bones or lungs.
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates
 The good news about prostate cancer is that it usually grows slowly. And 9 out of 10 cases are found in the early stages. Overall, the 5-year relative survival rate is 100% for men with disease confined to the prostate or nearby tissues, and many men live much longer. When the disease has spread to distant areas, that figure drops to 28%. But these numbers are based on men diagnosed at least 5 years ago. The outlook may be better for men diagnosed and treated today.
The good news about prostate cancer is that it usually grows slowly. And 9 out of 10 cases are found in the early stages. Overall, the 5-year relative survival rate is 100% for men with disease confined to the prostate or nearby tissues, and many men live much longer. When the disease has spread to distant areas, that figure drops to 28%. But these numbers are based on men diagnosed at least 5 years ago. The outlook may be better for men diagnosed and treated today.
Treatment: Watchful Waiting
 With low-risk cancer, one option is to watch and wait. This is determined by your biopsy, PSA test, and Gleason scores. Your doctor will order periodic testing. Other treatments — with the risk of sexual or urinary problems — may not be necessary. Some men who are older or have serious health conditions may not need treatment. However, more aggressive treatment is usually recommended for younger men or those with more aggressive disease.
With low-risk cancer, one option is to watch and wait. This is determined by your biopsy, PSA test, and Gleason scores. Your doctor will order periodic testing. Other treatments — with the risk of sexual or urinary problems — may not be necessary. Some men who are older or have serious health conditions may not need treatment. However, more aggressive treatment is usually recommended for younger men or those with more aggressive disease.
Treatment: Radiation Therapy
 External beam radiation to kill cancer cells can be used as a first treatment or after prostate cancer surgery. It can also help relieve bone pain from the spread of cancer. In brachytherapy, tiny radioactive pellets about the size of a grain of rice are inserted into the prostate. Both methods can impair erectile function. Fatigue, urinary problems, and diarrhea are other possible side effects.
External beam radiation to kill cancer cells can be used as a first treatment or after prostate cancer surgery. It can also help relieve bone pain from the spread of cancer. In brachytherapy, tiny radioactive pellets about the size of a grain of rice are inserted into the prostate. Both methods can impair erectile function. Fatigue, urinary problems, and diarrhea are other possible side effects.
There are some centers that provide proton therapy (a form of radiation therapy) for prostate cancer.
Treatment: Surgery
Removing the prostate, or radical prostatectomy, is used to eliminate the cancer when it is confined to the prostate. New techniques use smaller incisions and seek to avoid damaging nearby nerves. If lymph nodes are also cancerous, prostatectomy may not be the best option. Surgery may impair urinary and sexual function, but both can improve over time.
Treatment: Hormone Therapy
 Hormone therapy may shrink or slow the growth of cancer, but unless it is used with another therapy it will not eliminate the cancer. Drugs or hormones block or stop the production of testosterone and other male hormones, called androgens. Side effects can include hot flashes, growth of breast tissue, weight gain, and impotence.
Hormone therapy may shrink or slow the growth of cancer, but unless it is used with another therapy it will not eliminate the cancer. Drugs or hormones block or stop the production of testosterone and other male hormones, called androgens. Side effects can include hot flashes, growth of breast tissue, weight gain, and impotence.
Treatment: Chemotherapy
 Chemotherapy kills cancer cells throughout the body, including those outside the prostate, so it is used to treat more advanced cancer and cancer that did not respond to hormone therapy. Treatment is usually intravenous and is given in cycles lasting 3-6 months. Because the chemotherapy kills other fast-growing cells in the body, you may have hair loss and mouth sores. Other side effects include nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
Chemotherapy kills cancer cells throughout the body, including those outside the prostate, so it is used to treat more advanced cancer and cancer that did not respond to hormone therapy. Treatment is usually intravenous and is given in cycles lasting 3-6 months. Because the chemotherapy kills other fast-growing cells in the body, you may have hair loss and mouth sores. Other side effects include nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
Treatment: Cryotherapy
 Cryotherapy freezes and kills cancerous cells within the prostate (like the highly magnified cells shown here.) It is not as widely used because little is known about its long-term effectiveness. It’s less invasive than surgery, with a shorter recovery time. Because the freezing damages nerves, as many as 80% of men become impotent after cryosurgery. There can be temporary pain and burning sensations in the bladder and bowel.
Cryotherapy freezes and kills cancerous cells within the prostate (like the highly magnified cells shown here.) It is not as widely used because little is known about its long-term effectiveness. It’s less invasive than surgery, with a shorter recovery time. Because the freezing damages nerves, as many as 80% of men become impotent after cryosurgery. There can be temporary pain and burning sensations in the bladder and bowel.
Treatment: Prostate Cancer Vaccine
 This vaccine is designed to treat, not prevent, prostate cancer by spurring your body’s immune system to attack prostate cancer cells. Immune cells are removed from your blood, activated to fight cancer, and infused back into the blood. Three cycles occur in one month. It’s used for advanced prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone therapy. Mild side effects can occur such as fatigue, nausea, and fever.
This vaccine is designed to treat, not prevent, prostate cancer by spurring your body’s immune system to attack prostate cancer cells. Immune cells are removed from your blood, activated to fight cancer, and infused back into the blood. Three cycles occur in one month. It’s used for advanced prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone therapy. Mild side effects can occur such as fatigue, nausea, and fever.
Hope for Advanced Cancer
 Your doctor will continue to monitor your PSA levels and may perform other tests after treatment for prostate cancer. If it recurs or spreads to other parts of the body, additional treatment may be recommended. Lifestyle choices may matter, too. One study found that prostate cancer survivors who exercised regularly had a lower risk of dying, for example.
Your doctor will continue to monitor your PSA levels and may perform other tests after treatment for prostate cancer. If it recurs or spreads to other parts of the body, additional treatment may be recommended. Lifestyle choices may matter, too. One study found that prostate cancer survivors who exercised regularly had a lower risk of dying, for example.
Coping With Erectile Dysfunction
 Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common side effect of prostate cancer treatments. Generally, erectile function improves within two years after surgery. Improvement may be better for younger men than for those over age 70. You also may benefit from ED medications. Other treatments, such as injection therapy and vacuum devices, may help.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common side effect of prostate cancer treatments. Generally, erectile function improves within two years after surgery. Improvement may be better for younger men than for those over age 70. You also may benefit from ED medications. Other treatments, such as injection therapy and vacuum devices, may help.
Food for Health
 A cancer-conscious diet may be the best choice for survivors who want to bolster their health and those hoping to lower their risk. That means:
A cancer-conscious diet may be the best choice for survivors who want to bolster their health and those hoping to lower their risk. That means:
- Five or more fruits and veggies a day
- Whole grains instead of white flour or white rice
- Limit high-fat meat
- Limit or eliminate processed meat (hot dogs, cold cuts, bacon)
- Limit alcohol to 1-2 drinks per day (if you drink)
Foods high in folate may have some action against prostate cancer (such as spinach, orange juice, lentils). Studies found mixed results on lycopene, an antioxidant found in tomatoes.
Source- http://www.webmd.com/prostate-cancer/ss/slideshow-prostate-cancer-overview?ecd=wnl_men_012517&ctr=wnl-men-012517_nsl-ld-stry_1&mb=0Pr4CIOfW73AFmF7R4FSJeHnVev1imbCwl%2fJ9StOSgE%3d



 the primary condition (the cause of encephalopathy) and the encephalopathy itself. The most frequently utilized tests are listed below that may help to diagnose diabetic encephalopathy:
the primary condition (the cause of encephalopathy) and the encephalopathy itself. The most frequently utilized tests are listed below that may help to diagnose diabetic encephalopathy:









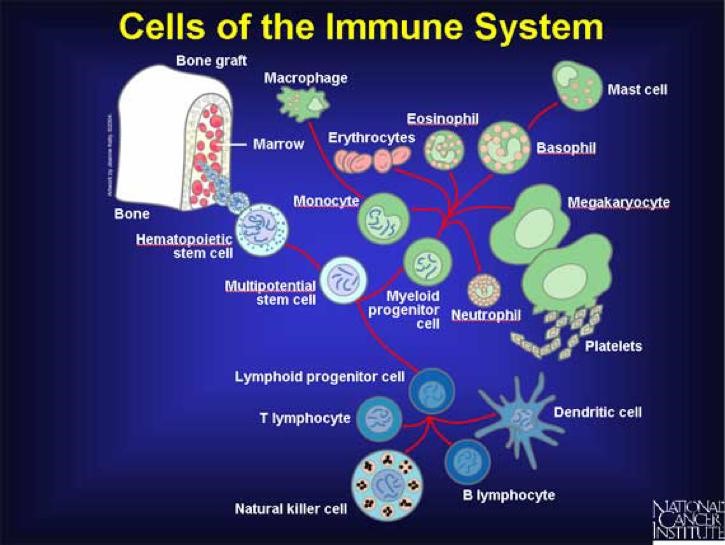 If the immune system is able to recognize and kill cancer cells, why do people get cancer?
If the immune system is able to recognize and kill cancer cells, why do people get cancer? 
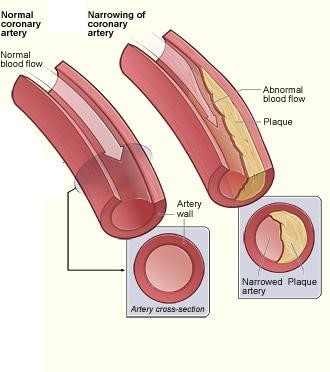
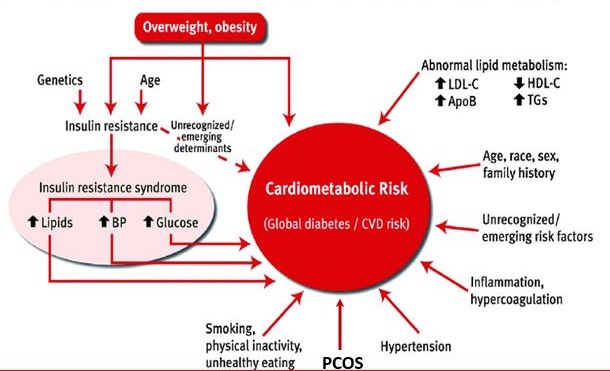
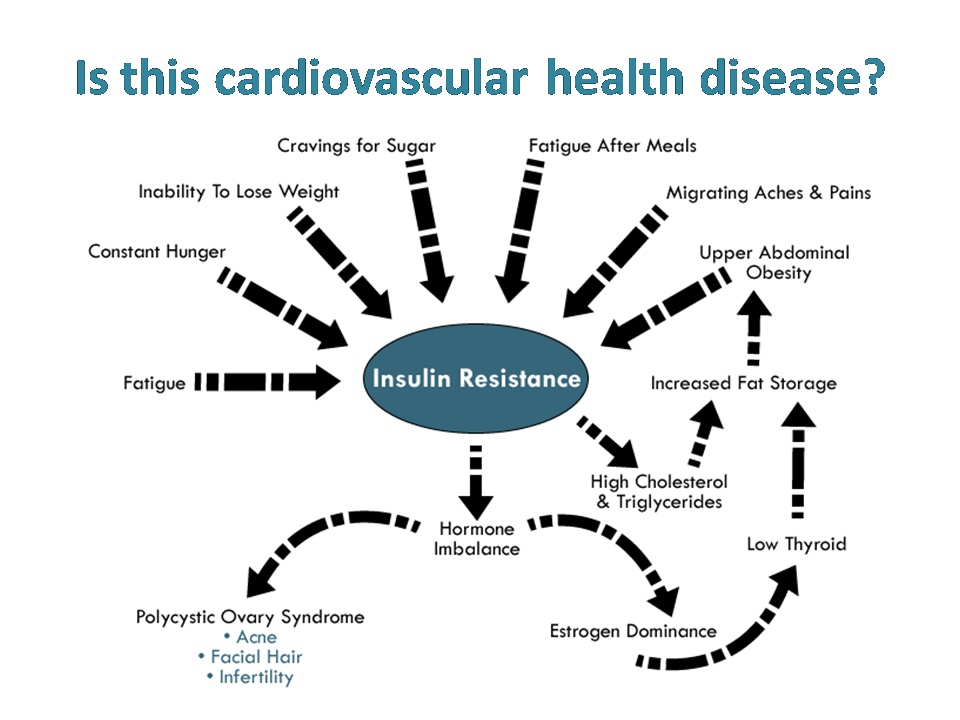





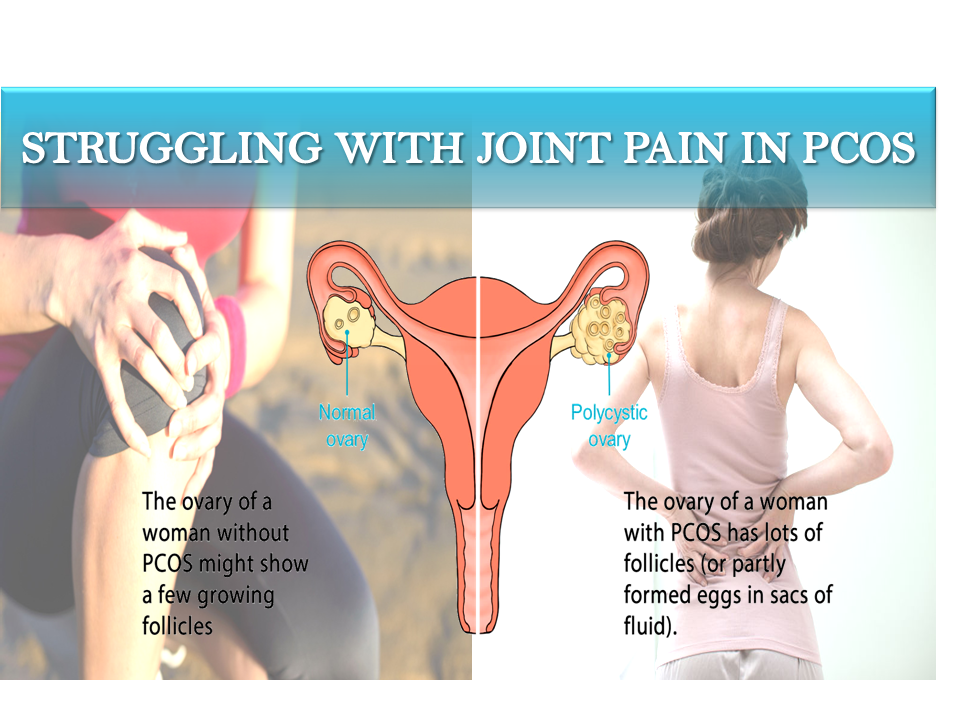

 Tender, warm, swollen joints
Tender, warm, swollen joints

















 Self-management is seen as a key capability for Patient Empowerment and emphasizes that persons with chronic diseases has the central role in managing their health.
Self-management is seen as a key capability for Patient Empowerment and emphasizes that persons with chronic diseases has the central role in managing their health. Only the internet allows us to set up an independent global diabetological service. The only thing users would need a computer and access to the internet. This service can serve unlimited number of people in the world along with medical consultation.
Only the internet allows us to set up an independent global diabetological service. The only thing users would need a computer and access to the internet. This service can serve unlimited number of people in the world along with medical consultation.





 Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil and avanafil) improve the relaxation of smooth muscle. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors are also contra-indicated in patients in whom vasodilation or sexual activity are inadvisable, and where there is previous history of non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy, hypotension.
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil and avanafil) improve the relaxation of smooth muscle. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors are also contra-indicated in patients in whom vasodilation or sexual activity are inadvisable, and where there is previous history of non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy, hypotension.


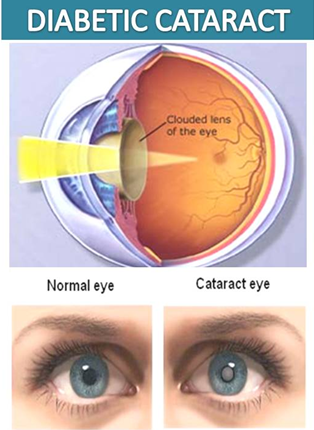
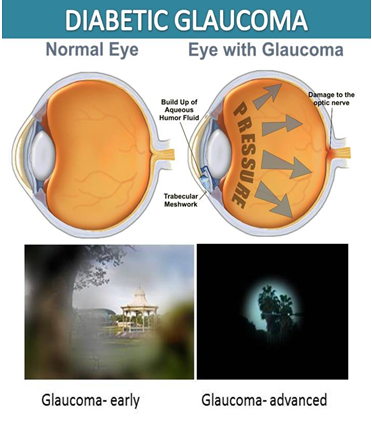

 The prostate can grow larger as men age, sometimes pressing on the bladder or urethra and causing symptoms similar to prostate cancer. This is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It’s not cancer and can be treated if symptoms become bothersome. A third problem that can cause urinary symptoms is prostatitis. This inflammation or infection may also cause a fever and in many cases is treated with medication.
The prostate can grow larger as men age, sometimes pressing on the bladder or urethra and causing symptoms similar to prostate cancer. This is called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It’s not cancer and can be treated if symptoms become bothersome. A third problem that can cause urinary symptoms is prostatitis. This inflammation or infection may also cause a fever and in many cases is treated with medication. Growing older is the greatest risk factor for prostate cancer, particularly after age 50. After age 70, studies suggest that most men have some form of prostate cancer, though there may be no outward symptoms. Family history increases a man’s risk: having a father or brother with prostate cancer doubles the risk. African-Americans are at high risk and have the highest rate of prostate cancer in the world.
Growing older is the greatest risk factor for prostate cancer, particularly after age 50. After age 70, studies suggest that most men have some form of prostate cancer, though there may be no outward symptoms. Family history increases a man’s risk: having a father or brother with prostate cancer doubles the risk. African-Americans are at high risk and have the highest rate of prostate cancer in the world.
 Here are some things that will not cause prostate cancer: Too much sex, a vasectomy, and masturbation. If you have an enlarged prostate (BPH), that does not mean you are at greater risk of developing prostate cancer. Researchers are still studying whether alcohol use, STDs, or prostatitis play a role in the development of prostate cancer.
Here are some things that will not cause prostate cancer: Too much sex, a vasectomy, and masturbation. If you have an enlarged prostate (BPH), that does not mean you are at greater risk of developing prostate cancer. Researchers are still studying whether alcohol use, STDs, or prostatitis play a role in the development of prostate cancer. Screening tests are available to find prostate cancer early, but government guidelines don’t call for routine testing in men at any age. The tests may find cancers that are so slow-growing that medical treatments would offer no benefit. And the treatments themselves can have serious side effects. The American Cancer Society advises men to talk with a doctor about screening tests, beginning at:
Screening tests are available to find prostate cancer early, but government guidelines don’t call for routine testing in men at any age. The tests may find cancers that are so slow-growing that medical treatments would offer no benefit. And the treatments themselves can have serious side effects. The American Cancer Society advises men to talk with a doctor about screening tests, beginning at: Your doctor may initially do a digital rectal exam (DRE) to feel for bumps or hard spots on the prostate. After a discussion with your doctor, a blood test can be used to measure prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a protein produced by prostate cells. An elevated level may indicate a higher chance that you have cancer, but you can have a high level and still be cancer-free. It is also possible to have a normal PSA and have prostate cancer.
Your doctor may initially do a digital rectal exam (DRE) to feel for bumps or hard spots on the prostate. After a discussion with your doctor, a blood test can be used to measure prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a protein produced by prostate cells. An elevated level may indicate a higher chance that you have cancer, but you can have a high level and still be cancer-free. It is also possible to have a normal PSA and have prostate cancer. A normal PSA level is considered to be under 4 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) of blood, while a PSA above 10 suggests a high risk of cancer. But there are many exceptions:
A normal PSA level is considered to be under 4 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) of blood, while a PSA above 10 suggests a high risk of cancer. But there are many exceptions: If a physical exam or PSA test suggests a problem, your doctor may recommend a biopsy. A needle is inserted either through the rectum wall or the skin between the rectum and scrotum. Multiple small tissue samples are removed and examined under a microscope. A biopsy is the best way to detect cancer and predict whether it is slow-growing or aggressive.
If a physical exam or PSA test suggests a problem, your doctor may recommend a biopsy. A needle is inserted either through the rectum wall or the skin between the rectum and scrotum. Multiple small tissue samples are removed and examined under a microscope. A biopsy is the best way to detect cancer and predict whether it is slow-growing or aggressive. A pathologist looks for cell abnormalities and “grades” the tissue sample from 1 to 5. The sum of two Gleason grades is the Gleason score. These scores help determine the chances of the cancer spreading. They range from 2, less aggressive, to 10, a very aggressive cancer. Gleason scores helps guide the type of treatment your doctor will recommend.
A pathologist looks for cell abnormalities and “grades” the tissue sample from 1 to 5. The sum of two Gleason grades is the Gleason score. These scores help determine the chances of the cancer spreading. They range from 2, less aggressive, to 10, a very aggressive cancer. Gleason scores helps guide the type of treatment your doctor will recommend. Some men may need additional tests to see if the cancer has spread beyond the prostate. These can include ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan (seen here). A radionuclide bone scan traces an injection of low-level radioactive material to help detect cancer that has spread to the bone.
Some men may need additional tests to see if the cancer has spread beyond the prostate. These can include ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan (seen here). A radionuclide bone scan traces an injection of low-level radioactive material to help detect cancer that has spread to the bone. Staging is used to describe how far prostate cancer has spread (metastasized) and to help determine the best treatment.
Staging is used to describe how far prostate cancer has spread (metastasized) and to help determine the best treatment. The good news about prostate cancer is that it usually grows slowly. And 9 out of 10 cases are found in the early stages. Overall, the 5-year relative survival rate is 100% for men with disease confined to the prostate or nearby tissues, and many men live much longer. When the disease has spread to distant areas, that figure drops to 28%. But these numbers are based on men diagnosed at least 5 years ago. The outlook may be better for men diagnosed and treated today.
The good news about prostate cancer is that it usually grows slowly. And 9 out of 10 cases are found in the early stages. Overall, the 5-year relative survival rate is 100% for men with disease confined to the prostate or nearby tissues, and many men live much longer. When the disease has spread to distant areas, that figure drops to 28%. But these numbers are based on men diagnosed at least 5 years ago. The outlook may be better for men diagnosed and treated today. With low-risk cancer, one option is to watch and wait. This is determined by your biopsy, PSA test, and Gleason scores. Your doctor will order periodic testing. Other treatments — with the risk of sexual or urinary problems — may not be necessary. Some men who are older or have serious health conditions may not need treatment. However, more aggressive treatment is usually recommended for younger men or those with more aggressive disease.
With low-risk cancer, one option is to watch and wait. This is determined by your biopsy, PSA test, and Gleason scores. Your doctor will order periodic testing. Other treatments — with the risk of sexual or urinary problems — may not be necessary. Some men who are older or have serious health conditions may not need treatment. However, more aggressive treatment is usually recommended for younger men or those with more aggressive disease. External beam radiation to kill cancer cells can be used as a first treatment or after prostate cancer surgery. It can also help relieve bone pain from the spread of cancer. In brachytherapy, tiny radioactive pellets about the size of a grain of rice are inserted into the prostate. Both methods can impair erectile function. Fatigue, urinary problems, and diarrhea are other possible side effects.
External beam radiation to kill cancer cells can be used as a first treatment or after prostate cancer surgery. It can also help relieve bone pain from the spread of cancer. In brachytherapy, tiny radioactive pellets about the size of a grain of rice are inserted into the prostate. Both methods can impair erectile function. Fatigue, urinary problems, and diarrhea are other possible side effects. Hormone therapy may shrink or slow the growth of cancer, but unless it is used with another therapy it will not eliminate the cancer. Drugs or hormones block or stop the production of testosterone and other male hormones, called androgens. Side effects can include hot flashes, growth of breast tissue, weight gain, and impotence.
Hormone therapy may shrink or slow the growth of cancer, but unless it is used with another therapy it will not eliminate the cancer. Drugs or hormones block or stop the production of testosterone and other male hormones, called androgens. Side effects can include hot flashes, growth of breast tissue, weight gain, and impotence. Chemotherapy kills cancer cells throughout the body, including those outside the prostate, so it is used to treat more advanced cancer and cancer that did not respond to hormone therapy. Treatment is usually intravenous and is given in cycles lasting 3-6 months. Because the chemotherapy kills other fast-growing cells in the body, you may have hair loss and mouth sores. Other side effects include nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
Chemotherapy kills cancer cells throughout the body, including those outside the prostate, so it is used to treat more advanced cancer and cancer that did not respond to hormone therapy. Treatment is usually intravenous and is given in cycles lasting 3-6 months. Because the chemotherapy kills other fast-growing cells in the body, you may have hair loss and mouth sores. Other side effects include nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. Cryotherapy freezes and kills cancerous cells within the prostate (like the highly magnified cells shown here.) It is not as widely used because little is known about its long-term effectiveness. It’s less invasive than surgery, with a shorter recovery time. Because the freezing damages nerves, as many as 80% of men become impotent after cryosurgery. There can be temporary pain and burning sensations in the bladder and bowel.
Cryotherapy freezes and kills cancerous cells within the prostate (like the highly magnified cells shown here.) It is not as widely used because little is known about its long-term effectiveness. It’s less invasive than surgery, with a shorter recovery time. Because the freezing damages nerves, as many as 80% of men become impotent after cryosurgery. There can be temporary pain and burning sensations in the bladder and bowel. This vaccine is designed to treat, not prevent, prostate cancer by spurring your body’s immune system to attack prostate cancer cells. Immune cells are removed from your blood, activated to fight cancer, and infused back into the blood. Three cycles occur in one month. It’s used for advanced prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone therapy. Mild side effects can occur such as fatigue, nausea, and fever.
This vaccine is designed to treat, not prevent, prostate cancer by spurring your body’s immune system to attack prostate cancer cells. Immune cells are removed from your blood, activated to fight cancer, and infused back into the blood. Three cycles occur in one month. It’s used for advanced prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone therapy. Mild side effects can occur such as fatigue, nausea, and fever. Your doctor will continue to monitor your PSA levels and may perform other tests after treatment for prostate cancer. If it recurs or spreads to other parts of the body, additional treatment may be recommended. Lifestyle choices may matter, too. One study found that prostate cancer survivors who exercised regularly had a lower risk of dying, for example.
Your doctor will continue to monitor your PSA levels and may perform other tests after treatment for prostate cancer. If it recurs or spreads to other parts of the body, additional treatment may be recommended. Lifestyle choices may matter, too. One study found that prostate cancer survivors who exercised regularly had a lower risk of dying, for example. Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common side effect of prostate cancer treatments. Generally, erectile function improves within two years after surgery. Improvement may be better for younger men than for those over age 70. You also may benefit from ED medications. Other treatments, such as injection therapy and vacuum devices, may help.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common side effect of prostate cancer treatments. Generally, erectile function improves within two years after surgery. Improvement may be better for younger men than for those over age 70. You also may benefit from ED medications. Other treatments, such as injection therapy and vacuum devices, may help. A cancer-conscious diet may be the best choice for survivors who want to bolster their health and those hoping to lower their risk. That means:
A cancer-conscious diet may be the best choice for survivors who want to bolster their health and those hoping to lower their risk. That means:


 Aerobic exercise helps the body to useinsulin It makes the heart and bones strong, relieves stress, improves blood circulation and reduces the risk of heart disease by lowering blood glucose and blood pressure and improving cholesterol levels.
Aerobic exercise helps the body to useinsulin It makes the heart and bones strong, relieves stress, improves blood circulation and reduces the risk of heart disease by lowering blood glucose and blood pressure and improving cholesterol levels. Strength training (also called resistance training) makes the body more sensitive to insulin and can lower bloodglucose. It helps to maintain and build strong muscles and bones, reducing the risk for osteoporosis and bone fractures. The more muscle you have, the more calories you burn – even when your body is at rest.
Strength training (also called resistance training) makes the body more sensitive to insulin and can lower bloodglucose. It helps to maintain and build strong muscles and bones, reducing the risk for osteoporosis and bone fractures. The more muscle you have, the more calories you burn – even when your body is at rest. If you are sitting for a long time, such as working at a desk or watching TV, do some light activity for 3 minutes or more every half hour to maintain the blood glucose levels.
If you are sitting for a long time, such as working at a desk or watching TV, do some light activity for 3 minutes or more every half hour to maintain the blood glucose levels.

