[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]THE CO-EXISTENCE OF DISEASES MEANS THE PRESENCE OF MULTIPLE DISEASES AT ONE TIME. In that way, the poly cystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hypothyroidism co-exist. Generally it has been observed that long-term untreated hypothyroidism always generate PCOS in females due to the imbalance of hormones in thyroid gland.
HYPOTHYROIDISM is the condition when the thyroid gland is not producing sufficient thyroid hormone. Thyroid gland is an organ of the body located in the front lower part of the neck. Hormones produced by this gland i.e. triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), travel through the bloodstream and get circulated in every part of the body. Thus, thyroid gland affects every part of the body. In hypothyroidism, there occurs imbalance in the levels of hormones inside body which causes many auto-immune diseases too.
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME (PCOS) is one such condition which is affected highly by the imbalance of hormones. Testosterone is one of those hormones. Increase in testosterone (male hormone) inside females causes the reproductive system to become infertile along with the development of multiple cysts in the ovaries. This worsens the condition of PCOS.
Thus, hypothyroidism gives rise to PCOS inside females. It has been seen that thyroid disorders and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are two of the most common endocrine disorders in the general population.
WHAT COULD BE THE REASON BEHIND DEVELOPMENT OF PCOS DUE TO HYPOTHYROIDISM?
One reason has been given that increase in testosterone levels causes PCOS in hypothyroid-affecting females.
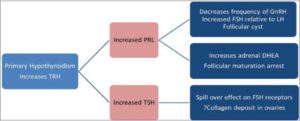
Another reason is the rise in thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). Rise in thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in primary hypothyroidism leads to increased prolactin and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Prolactin contributes toward polycystic ovarian syndrome by inhibiting ovulation as a result of the change in the ratio of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) and increased dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) from the adrenal gland. This causes PCOS in females suffering from hypothyroidism.
DIAGNOSIS Hypothyroidism
Blood test including:

- TSH:
- It measures how much T4 the thyroid is being asked to make. Abnormally high TSH levels may mean you have hypothyroidism.
- T4 tests(Free T4, free T4 index, total T4): It assesses the amount of T4 your thyroid is producing.
- Thyroid peroxidase antibody(anti-TPO) (TgAb): It checks for thyroid antibodies and to detect autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s disease.
- T3 and ReverseT3 (rT3): It assesses the amount of T3 your thyroid is producing and its ability to convert T4 to T3.
- Ultrasound: To detect cyst in the ovaries.
- Blood test including:
- Hormone levels: Such as thyroid hormones, testosterone levels, etc.
- Blood sugar: To check the common occurrence of insulin resistance in PCOS females.
- Lipid levels (LDL, Total Cholesterol, HDL and Triglycerides)
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT

To prevent the occurrence of PCOS developed along with hypothyroidism, it is better to cure the hypothyroidism as soon as possible. Possible prevention and treatment strategies for hypothyroidism are:
- Dietary modification
- Making dietary changes is the first line of defense in treating hypothyroidism.
- Carbohydrate: Reduce or eliminate caffeine and sugar, including refined carbohydrates like flour, which the body treats like sugar.
- Protein: Protein transports thyroid hormone to all the tissues and consumption of protein at each meal can help normalize thyroid function. Proteins include nuts and nut butters; quinoa; hormone- and antibiotic-free animal products (organic,grass-fed meats, eggs, and sustainably-farmed fish); and legumes.
- Glutathione: Glutathioneis a powerful antioxidant that strengthens the immune system and is one of the pillars of fighting Hashimoto’s. It can boost the body’s ability to modulate and regulate the immune system, dampen autoimmune flare-ups and protect and heal thyroid tissue.
- Medication Hypothyroidism can be easily treated using thyroid hormone medicine. The most effective and reliable thyroid replacement hormone is man-made (synthetic). Symptoms of hypothyroidism start to improve within the first week after you start treatment.

- Thyroid medicine levothyroxine is generally prescribed. Diets rich in soy and high fiber can interfere with levothyroxine absorption. Medications and supplements also can reduce absorption. These include calcium supplements, iron supplements, cholestyramine and aluminum hydroxide (present in some antacids).
- Lifestyle modification to manage PCOS

- Lifestyle modifications such as weight loss and increased exercise in combination with a change in diet consistently reduce the risk of diabetes. This approach has been found to be comparable to or better than treatment with medication and should therefore be considered first-line treatment in managing women with PCOS.
- These modifications have been effective in restoring ovulatory cycles and achieving pregnancy in obese women with PCOS. Weight loss in obese women with PCOS also improves hyper-androgenic features.
- Medication for PCOS

- Medical management of PCOS is aimed at the treatment of metabolic derangements, anovulation, hirsutism, and menstrual irregularity.
- The use of insulin-sensitizing drugs to improve insulin sensitivity is associated with a reduction in blood glucose levels, as well as improvement in both the ovulation rate and glucose tolerance.

- First-line medical therapy usually consists of an oral contraceptive to induce regular menses. The contraceptive not only inhibits ovarian androgen production but also increases sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) production.
- Treatment for ovulation induction when fertility is desired is clomiphene citrate.
- Other natural treatment strategies include consumption of food supplements such as fenugreek seed extract – Furocyst®, which has been clinically proven to treat PCOS and its symptoms.

For more info visit https://furocyst.com or