[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
symptoms of PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder in women causing enlarged ovaries with small cysts in the ovaries. Causes of PCOS are not clear but may be due to genetic and environmental factors.
Between 5% and 10% of women between 15 and 44 have PCOS. The incidence of PCOS is very common. But PCOS can happen at any age after puberty.
Women of all races and ethnicities are at risk of PCOS. The risk of PCOS may be higher if one is obese or if they have a mother, sister, or aunt with PCOS.
Some of the common PCOS symptoms are irregular menses, acne, prolonged menstruation, hirsutism (excessive hair in unwanted areas) and obesity among others. These PCOS symptoms are mostly physical. But PCOS symptoms can also be psychological like depression, difficulty in conceiving, etc.
Irregular periods are one of the most common symptom of PCOS and can be taken as the 1st signs of PCOS.
Most women face difficulty in getting pregnant with PCOS but by managing PCOS pregnancy symptoms, women might be able to conceive naturally and give birth to a healthy baby.
PCOS pregnancy symptoms are similar to normal pregnancy and a test to ascertain can be taken after a missed period.
It is very important to ascertain PCOS signs and symptoms in a timely fashion so that any further complications can be avoided and these can be managed effectively.
PCOS symptoms that are common:
- irregular menses
- excess androgen levels
- sleep apnea
- high stress levels
- high blood pressure
- skin tags
- infertility
- acne, oily skin, and dandruff
- high cholesterol and triglycerides
acanthosis nigricans, or dark patches of skin - fatigue
- female pattern balding
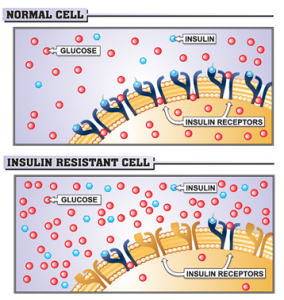
- insulin resistance
- type 2 diabetes
- pelvic pain
- depression and anxiety
- weight management difficulties including weight gain or difficulty losing weight
excessive facial and body hair growth, known as hirsutism - decreased libido
Some complications that can be a result of PCOS are:
- Infertility
- Gestational diabetes or pregnancy-induced high blood pressure
- Miscarriage or premature birth
- A severe liver inflammation caused by fat accumulation in the liver
- Metabolic syndrome — a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol or triglyceride levels that significantly increase your risk of cardiovascular disease
- Type 2 diabetes or prediabetes
- Sleep apnea
- Depression, anxiety and eating disorders
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Cancer of the uterine lining (endometrial cancer)
Thus, it is very important to consult a doctor as soon as you have the 1st signs of PCOS so that necessary steps can be taken to curb the complications of PCOS and for its effective management.
There is no single test to determine PCOS but range from physical exam, pelvic exam, pelvic ultrasound to blood tests.
Common PCOS treatment methods include birth control pills to regularize periods, medication to control blood glucose levels, statins to control high cholesterol, hormones to improve fertility as well as procedures to remove excessive body hair.
There is no comprehensive PCOS treatment available in the market as of now. The available PCOS treatment focuses on different aspects of PCOS and is not free of side effects.
Furocyst® is a patented and clinically evaluated, plant-based, natural comprehensive PCOS treatment. It is a pure fenugreek seeds extract and has no known side effects. It helps in reducing the ovary volume, decreasing cyst size, regularizing the periods and helps in regulating the blood glucose levels.
There is no PCOS cure as of now. PCOS can be managed and not reversed.
The best way to manage PCOS and its symptoms is through lifestyle modifications- healthy diet and regular exercise.
Even losing 10% of the body weight can make a great difference in your menstrual period and ovulation.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]


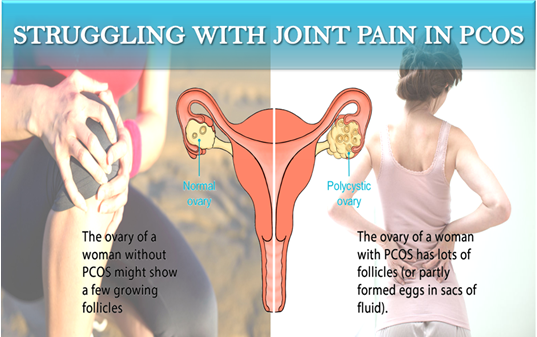



 Being active is one of the best things you can do for yourself, even if you have rheumatoid arthritis. You just have to know how to work within your limits because too much exercising involving stress on the joints can be harmful.
Being active is one of the best things you can do for yourself, even if you have rheumatoid arthritis. You just have to know how to work within your limits because too much exercising involving stress on the joints can be harmful.
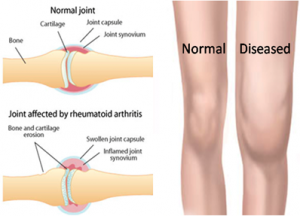
 Managing inflammation is a key component to living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This chronic condition results in the immune system attacking the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
Managing inflammation is a key component to living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This chronic condition results in the immune system attacking the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
 It has been reported that fenugreek is an effective remedy to treat
It has been reported that fenugreek is an effective remedy to treat
