UNDERSTANDING OBESITY
Obesity is a disease characterized by excessive body fat. People who are medically obese usually are affected by behavior, genetic and environmental factors that are difficult to control with dieting. Obesity increases the likelihood of certain diseases and other related health problems.
 Obesity is due to an individual taking in more calories than they burn over an extended period of time. These “extra” calories are stored as fat. Although there are several factors that can lead to this energy imbalance in obese individuals, the main contributors are behaviour, environment and genetics.
Obesity is due to an individual taking in more calories than they burn over an extended period of time. These “extra” calories are stored as fat. Although there are several factors that can lead to this energy imbalance in obese individuals, the main contributors are behaviour, environment and genetics.
Stages of overweight are medically defined by body mass index (BMI). An individual with a BMI of 25 to 29.9 kg/m2 is clinically classified as overweight. A BMI of 30 kg/m2 or more is classified as obese.
Obesity has been linked to a host of illnesses including
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease
- Breathing disorders
Rapid urbanization along with rising income and sedentary lifestyles have all been associated with rising levels of obesity.
SCENARIO OF OBESITY IN INDIA
 India is the third most obese country in the world. A country where 270 million people live below the ‘poverty line’, obesity seems to be a distant issue, meant for the rich kids of first world.
India is the third most obese country in the world. A country where 270 million people live below the ‘poverty line’, obesity seems to be a distant issue, meant for the rich kids of first world.
But India is under siege: junk food, alcohol and sedentary lifestyle are leading us to silent self destruction, making one in every five Indian men and women either obese or overweight.
A study published in the noted medical journal Lancet says India is just behind US and China in this global hazard list of top 10 countries with highest number of obese people.
WHAT ARE THE SOCIAL EFFECTS OF OBESITY?

Individuals affected by obesity often face obstacles far beyond health risks. Emotional suffering may be one of the most painful parts of obesity. Society often emphasizes the importance of physical appearance. As a result, people who are obese often face prejudice or discrimination in the job market, at school and in social situations.
IRVINGIA GABONENSIS: SOLUTION TO FIGHT OBESITY
African mango (Irvingia gabonensis) is a tree that is native to West African countries. The seeds from this tree are used to make medicine. Irvingia gabonensis has become so popular because it has been shown to help people lose weight.
HOW IRVINGIA GABONENSIS DOES HELP IN WEIGHT LOSS?

Researchers believe that African mango helps promote weight loss in several ways.
 It helps boost a person’s leptin level.
It helps boost a person’s leptin level.- Leptin is a hormone that helps suppress appetite. Obesity is associated with an increase in leptin levels, which is unusual for the standard mechanism of action in leptin. The reason associated to this is that obese individuals are believed to be resistant to the effects of leptin.
- Leptin resistance stimulates obesity. Therefore, leptin resistant people find it difficult to lose weight.
- A hearty appetite can prevent a person from reaching their weight loss goals.
- African mango helps delay stomach emptying. This helps prevent blood sugar spikes. Blood sugar spikes can lead to food cravings. Additionally, there has also been evidence to suggest that African mango helps increase the breakdown of fat.
SCIENTIFIC PROOF
There have been numerous studies done on African mango by researchers

- There was a clinical study done back in 2005 that tested the effectiveness of African mango on weight loss. There were a total of 40 participants. Twenty-eight of the participants took 350 mg of African mango abstract for one month while the other 12 were given a placebo. The results of the study were that the people who took the African mango extract were able to lose about 5% of their body weight. The subjects who were given a placebo only lost one percent of their body weight.
- Recently, there was another clinical study done on African mango. Half of the participants were given African mango while the other half was given a placebo. The results of the study were that the participants who took African mango were able to lose 7 pounds in just a month. The results of this study can be found in the Journal for American Health and Disease.
 It is easy to try one diet after another but this will never be a long-term solution. The right way to lose weight safely is to understand the science and research behind natural supplements and apart from this one should change eating habits and then ensure that those new, healthier eating habits become a way of life.
It is easy to try one diet after another but this will never be a long-term solution. The right way to lose weight safely is to understand the science and research behind natural supplements and apart from this one should change eating habits and then ensure that those new, healthier eating habits become a way of life.
There’s no point in adopting strict measure that prevent you from living life to the fullest. After all, food is there to be enjoyed. You need a way of eating where you can eat out with friends, socialize without having to give up the meal. Real and permanent fat loss (not just weight loss) has to be gradual and it takes time. The important thing, however, is that this approach works, and your weight will stay off.
FUROSLIM – Irvingia gabonensis helps to improve the sensitivity of leptin. Fortunately, it not only reverses leptin resistance, but also facilitates the breakdown of body fat by reducing an enzyme (glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) that enables glucose to be stored as triglyceride in adipocytes.
FUROSLIM – Irvingia gabonensis also increases the insulin-sensitizing hormone adiponectin and inhibits the digestive enzyme amylase that allows ingested carbohydrates to be broken down and absorbed into bloodstream.
REFERENCES


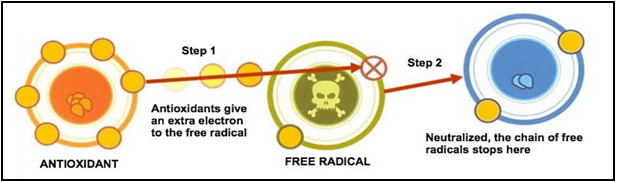


 Antioxidants in neurodegenerative diseases: Neuronal proteins and structural components get altered due to oxidative stress in different neurological disorders leading to neuro-inflammation and loss of cognitive function. Antioxidants are very effective for neuroprotection. Antioxidants target calcium mediated neurotoxicity and prevent the commencement of neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants also prevent the oxidation of proteins, lipid peroxidation and prevent the formation of free radicals, therefore acting as a barrier to the oxidative stress.
Antioxidants in neurodegenerative diseases: Neuronal proteins and structural components get altered due to oxidative stress in different neurological disorders leading to neuro-inflammation and loss of cognitive function. Antioxidants are very effective for neuroprotection. Antioxidants target calcium mediated neurotoxicity and prevent the commencement of neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants also prevent the oxidation of proteins, lipid peroxidation and prevent the formation of free radicals, therefore acting as a barrier to the oxidative stress. “You can’t possibly avoid free radicals but you can make sure you have enough antioxidants to minimize the damage”
“You can’t possibly avoid free radicals but you can make sure you have enough antioxidants to minimize the damage”
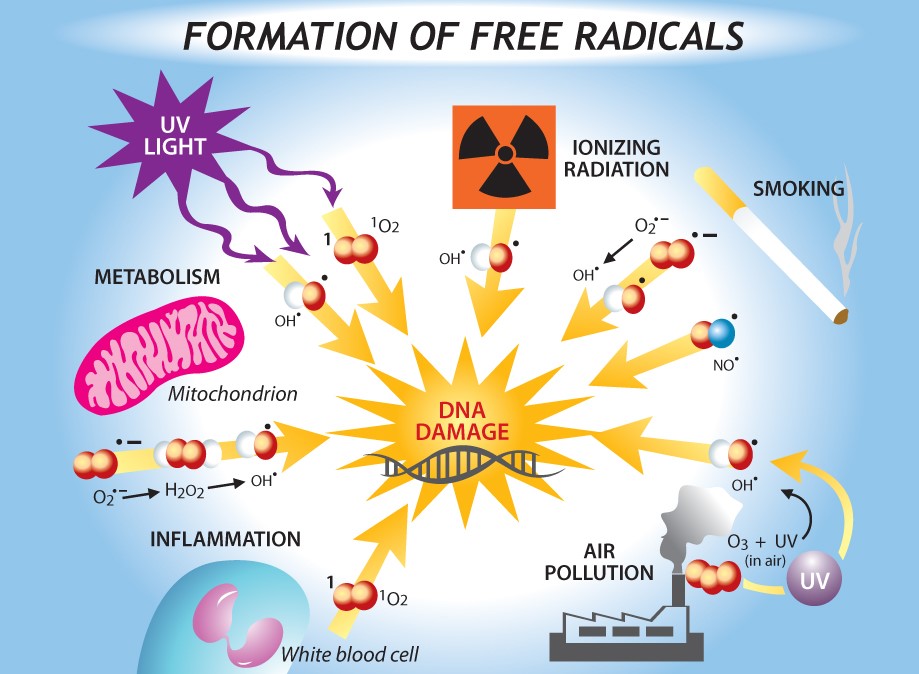
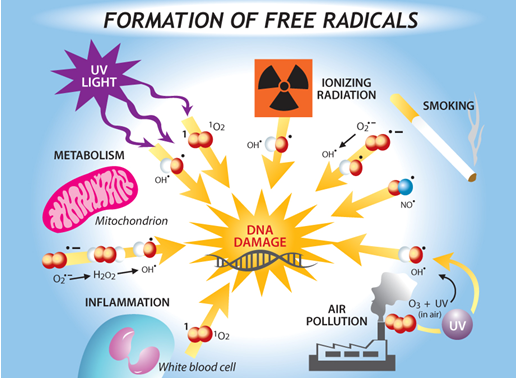
 can be ofmany shapes, sizes, and chemical configurations. What they all have in common is aninsatiable appetite for electrons, stealing them from close-by substances that will surrender This electrons’stealing can completely change the “loser’s” structure or function. Free radicals can damage or change the instructions coded in a strand of DNA causing numerous diseases including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and eye diseases such as cataract and age-related macular degeneration.
can be ofmany shapes, sizes, and chemical configurations. What they all have in common is aninsatiable appetite for electrons, stealing them from close-by substances that will surrender This electrons’stealing can completely change the “loser’s” structure or function. Free radicals can damage or change the instructions coded in a strand of DNA causing numerous diseases including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and eye diseases such as cataract and age-related macular degeneration.


 in nuts and seeds make them great sources of antioxidants.
in nuts and seeds make them great sources of antioxidants.



