HEALTH BENEFITS OF GREEN COFFEE BEANS

Green Coffee is derived from unrefined and unroasted seeds or beans from the popular Coffee fruit. The green coffee bean extract is proven to show miraculous health benefits especially in weight loss. It is gaining popularity as more & more research work is proving the HEALTH BENEFITS OF GREEN COFFEE BEANS.
Green coffee beans extract vs black coffee

While most of its health benefits are due to the presence of its major component, namely, chlorogenic acid, there are other HEALTH BENEFITS OF GREEN COFFEE BEANS which are because of some other compounds and factors. While the green coffee beans are in the natural state, the black coffee beans are roasted. Chlorogenic Acid is believed to be the main active component in green coffee beans but most part of the chlorogenic acids are destroyed when coffee is roasted Unlike green coffee beans, caffeine is present in a far greater percentage in black coffee, and the content of chlorogenic acids is lowered to 7% of the total bean weight.
How it works
It has been reported that the green coffee bean extract has a comparatively higher degree of absorption. Once green coffee bean extract is consumed, half the chlorogenic acid is quickly metabolized into caffeinated and ferulic acid, a very small percentage continues to function in the body in the original form, i.e CGA. The metabolism rate differs in individuals, but chlorogenic acid and its metabolites are detected in the body even 24 hours after administration. The other half is metabolized into benzoic (hippuric) acid.
The three major metabolites are responsible for the majority of HEALTH BENEFITS OF GREEN COFFEE BEANS.
Proven HEALTH BENEFITS OF GREEN COFFEE BEANS Extract
Green Coffee for Weight Loss
A study published in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine in march 2006 has stated that the daily consumption of green coffee bean capsules or extract in any form comparatively reduces the body fat as well as the fat composition present in the liver. The same experiment was conducted on other group using only the isolated chlorogenic acids and caffeine and the results were same. Thus, it was concluded that Chlorogenic Acids present in a green coffee bean can help in losing weight.
Reduces Risk of Diabetes

Regular consumption of green coffee beans extract reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and CGA is major bioactive compound in coffee that provides health benefits. It has been reported that daily consumption of 3 to 4 cups of decaffeinated coffee containing high percentage of CGA significantly reduces the risk for T2DM by 30% . Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is a great insulin sensitizer that improves the
insulin action. It had been reported that Chlorogenic acid (CGA) at a dose of 5 mg/kg body weight exerts antidiabetic effect in nicotinamide induced diabetic rats.
CGA is reported to attenuate intestinal glucose absorption, indicating a possible role for CGA as a glycaemic index lowering agent as well as helps in reducing the risk of developing T2DM.
It was reported that consuming CGA significantly reduced early fasting glucose and insulin responses in overweight men during an oral glucose tolerance test.
Many Clinical trials establish that Chlorogenic Acid in coffee is able to harmonize glucose intake and gastrointestinal hormone and insulin secretion in humans.
Reduces Risk of Heart Disease

Hypercholesterolemia is a major risk factor for the advancement of cardiovascular disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Chlorogenic Acids are hypoglycemic agents and can affect lipid metabolism.
CGA is effective in the case of weight gain and fat accumulation by restriction of fat absorption and activation of fat metabolism in the liver.
Antioxidant Benefits
Green Coffee Bean extract is a powerful antioxidant, which helps in averting the damages caused by free radicals. Green coffee is reported to prevent the propagation of cancer cells, thus suggesting that green coffee may have cancer preventing properties as well. Antioxidants also improve skin texture & prevent it from oxidative damage.
Improved Mood and Cognitive Performance
 Grecobe, the Green Coffee has recently been launched in the market as ready to drink sachets. It is a single ingredient product without any additives and excipients, thus ensuring better therapeutic value of each sachet. It’s a healthy drink, which is a taste paradise too.
Grecobe, the Green Coffee has recently been launched in the market as ready to drink sachets. It is a single ingredient product without any additives and excipients, thus ensuring better therapeutic value of each sachet. It’s a healthy drink, which is a taste paradise too.

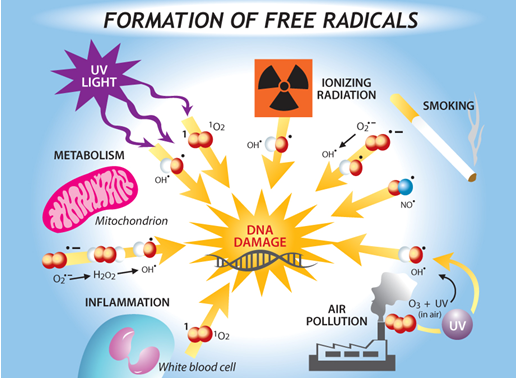
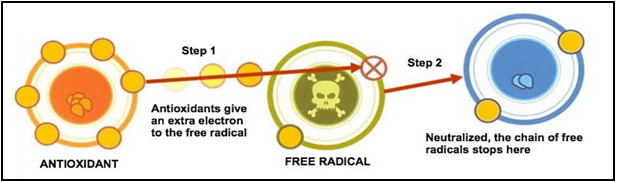


 Antioxidants in neurodegenerative diseases: Neuronal proteins and structural components get altered due to oxidative stress in different neurological disorders leading to neuro-inflammation and loss of cognitive function. Antioxidants are very effective for neuroprotection. Antioxidants target calcium mediated neurotoxicity and prevent the commencement of neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants also prevent the oxidation of proteins, lipid peroxidation and prevent the formation of free radicals, therefore acting as a barrier to the oxidative stress.
Antioxidants in neurodegenerative diseases: Neuronal proteins and structural components get altered due to oxidative stress in different neurological disorders leading to neuro-inflammation and loss of cognitive function. Antioxidants are very effective for neuroprotection. Antioxidants target calcium mediated neurotoxicity and prevent the commencement of neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants also prevent the oxidation of proteins, lipid peroxidation and prevent the formation of free radicals, therefore acting as a barrier to the oxidative stress. “You can’t possibly avoid free radicals but you can make sure you have enough antioxidants to minimize the damage”
“You can’t possibly avoid free radicals but you can make sure you have enough antioxidants to minimize the damage”
