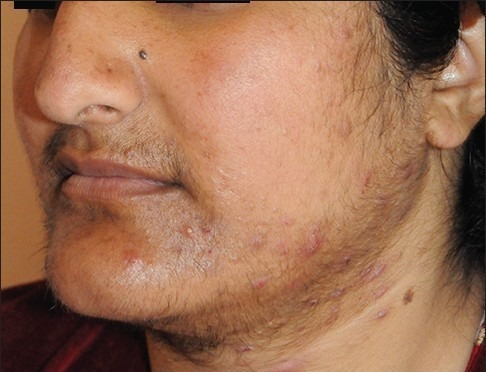
Hirsutism is the excessive hairiness on women on those parts of the body where hair normally is absent or minimal, such as beard or chest hair. It refers to a male pattern of body hair (androgenic hair) and it is therefore primarily of cosmetic and psychological concern. In 90% of the cases of Hirsutism, the women are tested positive for Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Hirsutism.
PCOS is one of the most common endocrine disorders affecting women. Reportedly, around 5- 10 per cent of women in India are affected with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS). One of the primary issues with PCOS is that the insulin producing cells are over responsive and create too much insulin, causing Hyperinsulinemia. The increase in insulin causes the ovaries to produce too much of testosterone, excess androgens cause ovarian cysts, acne and male pattern hair growth. Androgen acts on the growth phase of hair cycle, causing the hair to go from vellus hair (the light, thin hair that covers the body) to terminal hair (thick, dark hair). There are a variety of treatments available to treat hirsutism.
Hormonal Treatment
Birth control pills are the most commonly suggested hormonal treatment for hirsutism. Birth control pills work by decreasing the production of androgens or male hormones, by the ovaries. Anti-androgen medicines are also prescribed to treat hirsutism because it directly blocks the effects of androgens in hair follicles. But most important, these medications are prescribed to women who are not pregnant, nor planning to become pregnant. In patients who have an “overactive” adrenal gland, low doses of steroids may be prescribed to suppress their activity. Women taking steroids may experience dizziness during the day or have difficulty falling asleep. These drugs may have serious side effects, including weight gain, thinning of the skin and bones, and decreased defense against infection.
Hormone treatment generally prevents new terminal hairs from developing and may slow the growth rate of existing hairs. Generally about six months of hormone therapy is required before the rate of hair growth decreases significantly. It is usually not possible to cure the hormonal problem that causes hirsutism, ongoing medical treatment is required to manage it. Hirsutism will frequently return if medical treatment is stopped.
Hair Removal
There are many temporary and permanent hair-removing techniques that are used by the women experiencing Hirutism. Plucking, waxing, shaving and using of epilators are among the most common solutions for temporary hair removal.
There are two types of permanent hair removal methods: electrolysis and laser treatment.
Electrolysis uses a very fine needle, which is inserted into the hair follicle. A mild electric current is sent through the needle to permanently destroy the hair follicle’s ability to produce hair. Since follicles are treated one at a time, it is impractical to use electrolysis to treat very large areas of the body. Laser treatments may be used on large areas of the body, although their long term effectiveness is not as well documented as electrolysis. During laser hair treatment, a beam of light is passed through the skin to the hair follicle to destroy it. Both methods of hair reduction are moderately painful, depending on the area of skin being treated, and multiple treatments are usually required.
Eat Right
Eating plenty of foods that contain vitamin B, chromium and magnesium – may help prevent and treat hirsutism. One should avoid intake of fats and taking high calorie food in the evening. Regular intake of dietary supplement like FUROCYST can give positive results in PCOS management. FUROCYST is an innovative product (extracted and developed through a novel & innovative U.S. patented process) involving separations of active ingredients from the natural plant without affecting chemical properties of the active fractions. No chemicals are used. It is a natural and promising dietary supplement effective for management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) with proved safety and an efficacy rate of 94%.
IMAGE SOURCE: GOOGLE IMAGES