Diabetes is a long-term condition that causes a person’s blood sugar level to become too high. It is a metabolic disease and chronic disorder, which results from defects in insulin secretion or action.
Insulin is a hormone, which is secreted by pancreas and lowers the blood glucose level in the body. When insulin secretion or action is disturbed, diabetes mellitus develops.
DEPRESSION
It is a mood disorder and serious medical illness, which can alter the person’s thoughts, behaviour, feelings and sense of well-being. It is a disorder of brain, which can happen at any age, especially in teens and adults.
World Health Organisation (WHO) describes depression as the major cause of disability, which is estimated to account for 12% of the global burden of disease. It is reported to affect approximately 450 million people.
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN DIABETES AND DEPRESSION
Depression is a very drastic condition becoming common in the general population i.e. approximately 1 in 4 people experience depression in their life and people with diabetes are at more risk to develop depression i.e. up to 50% of people with diabetes are thought to have mental illness such as depression or anxiety. Depressive patients are also at higher risk of developing diabetes. It is also reported that untreated depression can make it difficult to manage diabetes.
CAUSES OF DEPRESSION IN DIABETES
- The hardship of managing diabetes can be stressful and can lead to symptoms of depression.
- Diabetes leads to many health complications that may worsen symptoms of depression.
- Family history of either condition
- Obesity
- Hypertension
- Inactivity
- Coronary artery disease
According to the above data, the complications of diabetes are major reason behind the development of depression. By treating diabetes or its complications can help in the management of depression too.
SYMPTOMS OF DEPRESSION IN DIABETES
The diagnosis of depression in a diabetic individual is important, which can be done by monitoring the symptoms of depression. These include:
- No longer finding pleasure in the activities that you once enjoyed
- Experiencing insomnia or sleeping too much
- Loss of appetite or binge eating
- Inability to concentrate
- Feeling lethargic
- Feeling anxious or nervous all the time
- Feeling isolated and alone
- Feeling sadness in the morning
- Feeling that you “never do anything right”
- Having suicidal thoughts
- Harming yourself
MANAGEMENT OF DIABETES AND DEPRESSION TOGETHER
Diabetes self–management programs
Diabetes self assessment programs can focus on behaviour and help the people to improve their fitness levels and manage weight loss and other cardiovascular disease risk factors. These programs also improve the quality of life and sense of well being of the affected person.
Diabetes self-management strategies include:
- Monitoring blood glucose levels on regular basis
- Monitoring weight gain/weight loss
- Regular exercise or other physical activities
- Healthy eating and planning of diet according to the blood glucose levels
- Regularity with anti-diabetic medications
- Consuming lesser carbohydrates

Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy reported to have improvements in depression patients, which has resulted in better diabetes management. Psychotherapy can be short term or long term.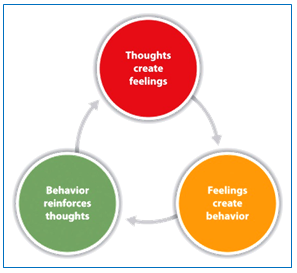
Goals of the psychotherapy include:
- Recognition of potential triggers
- Identification and replacement of unhealthy behaviors
- Development of positive relationship of patient with others
- To promote healthy problem-solving skills
Medication
- Anti-diabetic medication: For treating depression raised from the diabetic complications, it is better to treat diabetes first. When the diabetes will be treated, depression will automatically be cured. It is better to consume herbal supplements, which can prevent and treat diabetes with much lesser complications.
One such anti-diabetic herbal supplement is Fenfuro. Fenfuro is clinically proven and supported by six international patents for effective and safe management of blood glucose levels.
If cognitive behavioural therapy and anti-diabetic supplementation is not sufficient for the treatment of depression, then, psychotherapist can be consulted to treat with anti-depressant medications. Psychotherapist can prescribe from any of the following anti-depressant categories:
- Tricyclic anti-depressants: They work by boosting the levels of certain chemicals in the brain that help nerve cells to communicate with each other. If these chemicals are out of balance or don’t work like they should, messages might not make it through the brain correctly that can lead to depression.
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI): They affect the way in which brain uses a chemical called serotonin. Changing the balance of this chemical may help the brain cells to receive messages better and boost mood.
- Serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRI): They block the re-absorption of both serotonin and norepinephrine. Like SSRIs, they improve the way in which brain sends and receives messages.
These anti-depressants should only be consumed after consultation with psychotherapist. Some strong anti-depressants can cause diabetes. Due to this, doctors prescribe small doses initially and increase the dose on requirement.
REFERENCES
- https://wada-main-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/wada-tpg-diabetes_mellitus-3.0-en.pdf
- https://thebloodsugardiet.com/quizzes/type-2-diabetes-self-assessment-from-the-nhs/
- https://www.diabetesaustralia.com.au/depression-and-mental-health
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3626025/
- http://www.diabetesselfmanagement.com/blog/depression-and-type-2-diabetes-symptoms-or-disease/
- http://www.diabetes.co.uk/diabetes-and-depression.html
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/expert-answers/diabetes-and-depression/faq-20057904
- http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/complications/mental-health/depression.html?referrer=https://www.google.co.in/
- http://www.healthline.com/health/type-2-diabetes/depression#Treatment6
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3738724/
- http://www.webmd.com/diabetes/guide/coping-depression#2



